"Providing quality Healthcare that’s easily accessible" - Dr. T. Poonyane
Call
Call to book or to enquire
Virtual Consultation
ZOOM Video Call (Book an appointment first)
Send Queries
Send Us Your Questions Through Mail
Find Location
Navigate to our Location
“From the beginning, my goal was to be a ‘partner’ in your healthcare. I’m compassionate, well-trained, and want to provide you with the best care possible” - Dr. T. Poonyane
Procedures

Gynaecology
- Abnormal Bleeding
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Adolescent Gynaecology
- Botox for Painful Intercourse (Vulvodynia)
- Contraception (Family Planning)
- Endometriosis
- Cervix Screening
- Infertility
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Fibroid Treatment & Surgery
- Menopause Treatment
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Aesthetic/Cosmetic Gynaecology
- G-Spot Enhancement
- Labiaplasty
- Laser Genital Bleaching
- Laser Vaginal Tightening
- O-Shot for Vaginal Dryness

Obstetrics
- Pregnancy Confirmation
- Sonar Services
- Screening for chromosomal abnormalities
- Genetic Syndromes
- High Risk Pregnancy
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
- Normal Vaginal Delivery
- Caesarean section Delivery
Procedures Explained
Abnormal uterine bleeding is any heavy or unusual bleeding from the uterus (through your vagina). It can occur at any time during your monthly cycle, including during your normal menstrual period. Vaginal bleeding between periods is one symptom of abnormal uterine bleeding. Having extremely heavy bleeding during your period can also be considered abnormal uterine bleeding. Very heavy bleeding during a period and/or bleeding that lasts more than 7 days is called menorrhagia. For example, women may bleed enough to soak through 1 or more tampons or sanitary pads every hour.
In most women, abnormal uterine bleeding is caused by a hormone imbalance. When hormones are the problem, doctors call the problem dysfunctional uterine bleeding, or DUB. Abnormal bleeding caused by hormone imbalance is more common in teenagers or in women who are approaching menopause.
These are just a few of the problems that can cause abnormal uterine bleeding. These problems can occur at any age, but the likely cause of abnormal uterine bleeding usually depends on your age.
Women in their teens, 20s, and 30s
A common cause of abnormal bleeding in young women and teenagers is pregnancy. Many women have abnormal bleeding in the first few months of a normal pregnancy. Some birth control pills or the intrauterine device (IUD) can also cause abnormal bleeding.
Some young women who have abnormal uterine bleeding do not release an egg from their ovaries (called ovulation) during their menstrual cycle. This is common for teenagers who have just started getting their periods. This causes a hormone imbalance where the estrogen in your body makes the lining of your uterus (called the endometrium) grow until it gets too thick. When your body gets rid of this lining during your period, the bleeding will be very heavy. A hormone imbalance may also cause your body not to know when to shed the lining. This can cause irregular bleeding (“spotting”) between your periods.
Women in their 40s and early 50s
In the years before menopause and when menopause begins, women have months when they don’t ovulate. This can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, including heavy periods and lighter, irregular bleeding.
Thickening of the lining of the uterus is another cause of bleeding in women in their 40s and 50s. This thickening can be a warning of uterine cancer. If you have abnormal uterine bleeding and you’re in this age group, you need to tell your doctor about it. It may be a normal part of getting older, but it’s important to make sure uterine cancer isn’t the cause.
Women after menopause
Hormone replacement therapy is a common cause of uterine bleeding after menopause. Other causes include endometrial and uterine cancer. These cancers are more common in older women than in younger women. But cancer is not always the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. Many other problems can cause bleeding after menopause. For this reason, it’s important to talk to your doctor if you have any bleeding after menopause.
Tests I will conduct depend on your age. If you could be pregnant, I may order a pregnancy test. If your bleeding is heavy, in addition to other tests, I may want to check your blood count to make sure you don’t have a low blood count from the blood loss. This could lead to iron deficiency and anemia.
I may want to do an endometrial biopsy. This is a test of the uterine lining. It’s done by putting a thin plastic tube (called a catheter) into your uterus. I will use the catheter to remove a tiny piece of the uterine lining. I will send that lining to the lab for testing. The test will show if you have cancer or a change in the cells. A biopsy can be done in the practice and causes only mild pain.
Another test is a hysteroscopy. A thin tube with a tiny camera in it is put into your uterus. The camera lets me see the inside of your uterus. If anything abnormal shows up, I can get a biopsy.
Hormones are your body’s chemical messengers. Produced in the endocrine glands, these powerful chemicals travel around your bloodstream telling tissues and organs what to do. They help control many of your body’s major processes, including metabolism and reproduction.
When you have a hormonal imbalance, you have too much or too little of a certain hormone. Even tiny changes can have serious effects throughout your whole body.
Think of hormones like a cake recipe. Too much or too little of any one ingredient affects the final product. While some hormone levels fluctuate throughout your lifetime and may just be the result of natural aging, other changes occur when your endocrine glands get the recipe wrong.
Symptoms of a hormonal imbalance
Your hormones play an integral role in your overall health. Because of that, there’s a broad range of symptoms that could signal a hormonal imbalance. Your symptoms will depend on which hormones or glands aren’t working properly.
Common hormonal conditions affecting both men and women could cause any of the following symptoms:
- weight gain
- fatigue
- increased sensitivity to cold or heat
- constipation or more frequent bowel movements
- dry skin
- puffy face
- unexplained weight loss (sometimes sudden)
- increased or decreased heart rate
- muscle weakness
- frequent urination
- increased thirst
- muscle aches, tenderness, and stiffness
- pain, stiffness, or swelling in your joints
- thinning hair or fine, brittle hair
- increased hunger
- depression
- decreased sex drive
- nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- blurred vision
- sweating
- infertility
- a fatty hump between the shoulders
- rounded face
- purple or pink stretch marks
Symptoms
In women, the most commonTrusted Source hormonal imbalance is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Your normal hormonal cycle also changes naturally during:
- puberty
- pregnancy
- breastfeeding
- menopause
- heavy or irregular periods, including missed periods, stopped period, or frequent period
- hirsutism, or excessive hair on the face, chin, or other parts of the body
- acne on the face, chest, or upper back
- thinning hair or hair loss
- weight gain or trouble losing weight
- darkening of skin, especially along neck creases, in the groin, and underneath breasts
- skin tags
- vaginal dryness
- vaginal atrophy
- pain during sex
- night sweats
A screening Pap smear which returns an abnormal result may in some cases prompt the scheduling of a colposcopy exam of the cervix and / or vaginal tissues.
During a colposcopy exam, a speculum will be inserted as it is for a regular gynaecological exam. A diluted vinegar solution is placed on the cervix in order to allow a clear view of the cervix. This solution washes away mucus from the cervix and allows any abnormal cells to be more clearly visible during the exam. The cervix is visualized with the use of a colposcope, (a magnifying instrument) placed outside the vagina, allowing the doctor view of possible sources of abnormal cells.
If possible sources of abnormal cells are identified on the cervix or vaginal tissues, small biopsies of these areas may be performed. A small instrument may also be used to sample the tissue of the endocervical canal (the opening in the cervix) in order to ensure that abnormal cells are not found in an area not clearly visible with the colposcope. All samples obtained are then sent to a pathology laboratory and examined by a pathologist.
What should I expect during after a colposcopy?
You may have some vaginal bleeding. You also may have a dark discharge for a few days. This may occur from medication used to help stop bleeding at the biopsy site. While your cervix heals you will be instructed not to put anything into your vagina for a short time (no intercourse, no tampons, no douching). Depending on the results of a colposcopy your physician will recommend observation with a repeat Pap smear, medication or minor surgery called a LEEP or conization.
When to call the doctor?
- Heavy vaginal bleeding (using more than one maxi pad per hour)
- Severe lower abdominal pain
- Fever
- Chills
About me
Committed To OBGYN Excellence
I’m an avid Obstetrician and Gynaecologist FCOG (SA) adapt at caring for patients of diverse backgrounds and in settings of varying complexities. I completed my undergraduate degree (MBBCh) at the University of the Witwatersrand then furthered my studies in the field of Obstetrics & Gynaecology through the Colleges of Medicine of South Africa.
I’m Board Certified in high risk obstetrics, gynaecologic, urogynaecology, advanced laparoscopic, pelvic floor reconstruction and endoscopic surgery with experience in active general practice. Acquired extensive experience in OBGYN practice by providing high quality care to uncomplicated and high risk obstetric patients, performing delicate gynaecological surgeries and treating infertility. Earned a high quality reputation for confident high level clinical skills, judgment and medical problem solving in acute care situations with excellent surgical outcomes.
Affiliations







Qualifications
2006 – MBBCh, University of the Witwatersrand
2015 -MMed (O & G), University of the Witwatersrand
2015 – FCOG (SA), Colleges of Medicine
Profile
HPCSA Reg. # – MP0663409
Practice # – 0601241
Reviews From My Happy Patients
Creating Beautiful Pregnancies For Healthy Mommies and Babies
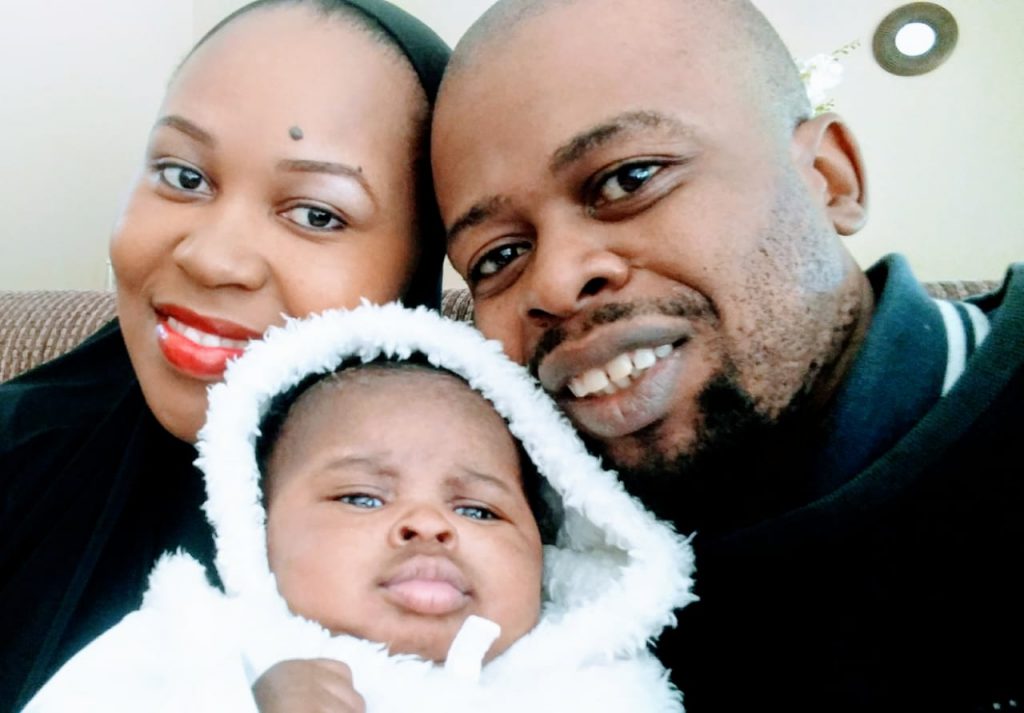


Mr. & Mrs. Matloha
We found the service of Dr Poonyane to be excellent, from the moment we first made contact we have encountered a friendly and professional service from all of the team. In particular we are so grateful to Dr Poonyane for the successful delivery of our first and second daughter, we cannot recommend him highly enough.
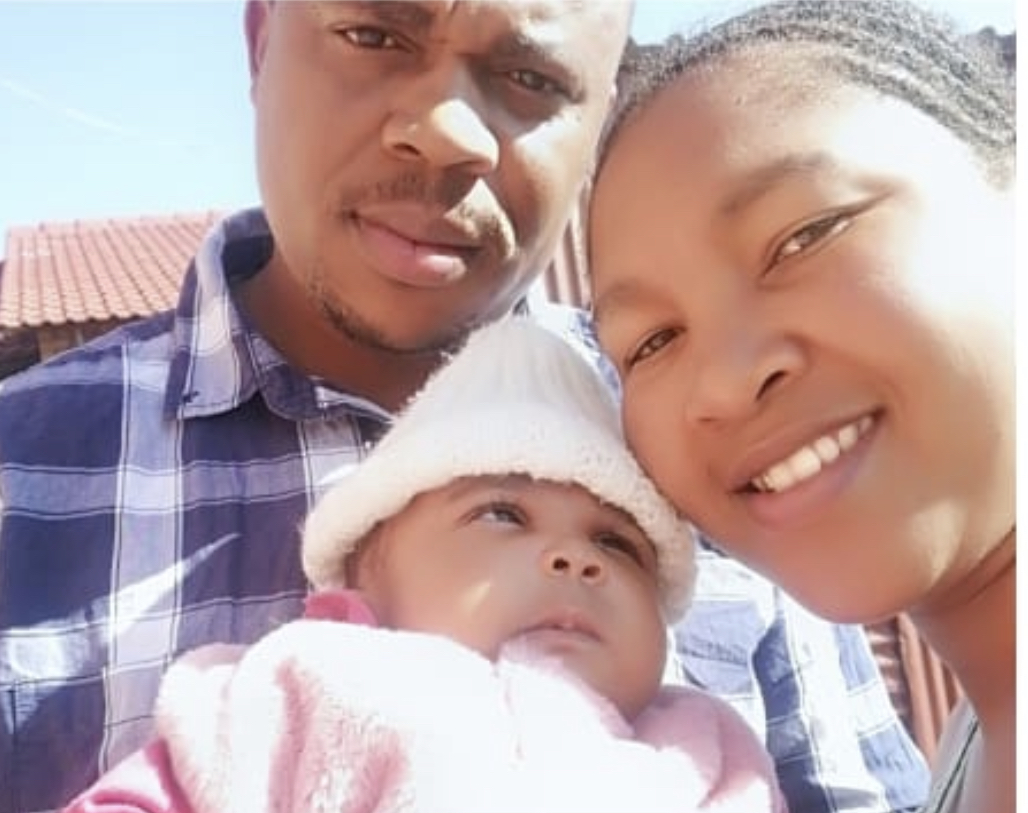


Robert & Thandi
Thank you so much to Dr. T Poonyane and his team for your wonderful care.We really appreciate and are thankful for you delivering our daughter Onkgahlile Tsoari at Mediclinic Vereeniging on the 28th of February 2020.
We felt blessed to have such a great Doctor taking care of us and making sure that we are happy at all times.
We wish all the best for Dr. Poonnyane and the team, continue to be blessing in others in your professions.
How To Find Us
Address:
Room 219, 2nd Floor
Block 1 Mediclinic Vereeniging
Corner Hofmeyer & Joubert Streets
Vereeniging
Contact Details
Office Tel: 016 440 5311 or 016 421 1314
E-mail: Reception@drpoonyane.com
E-mail: Thabane@drpoonyane.com
Working Hours:
Mediclinic Mondays, Tuesdays & Thursday 14:00 – 17:00
